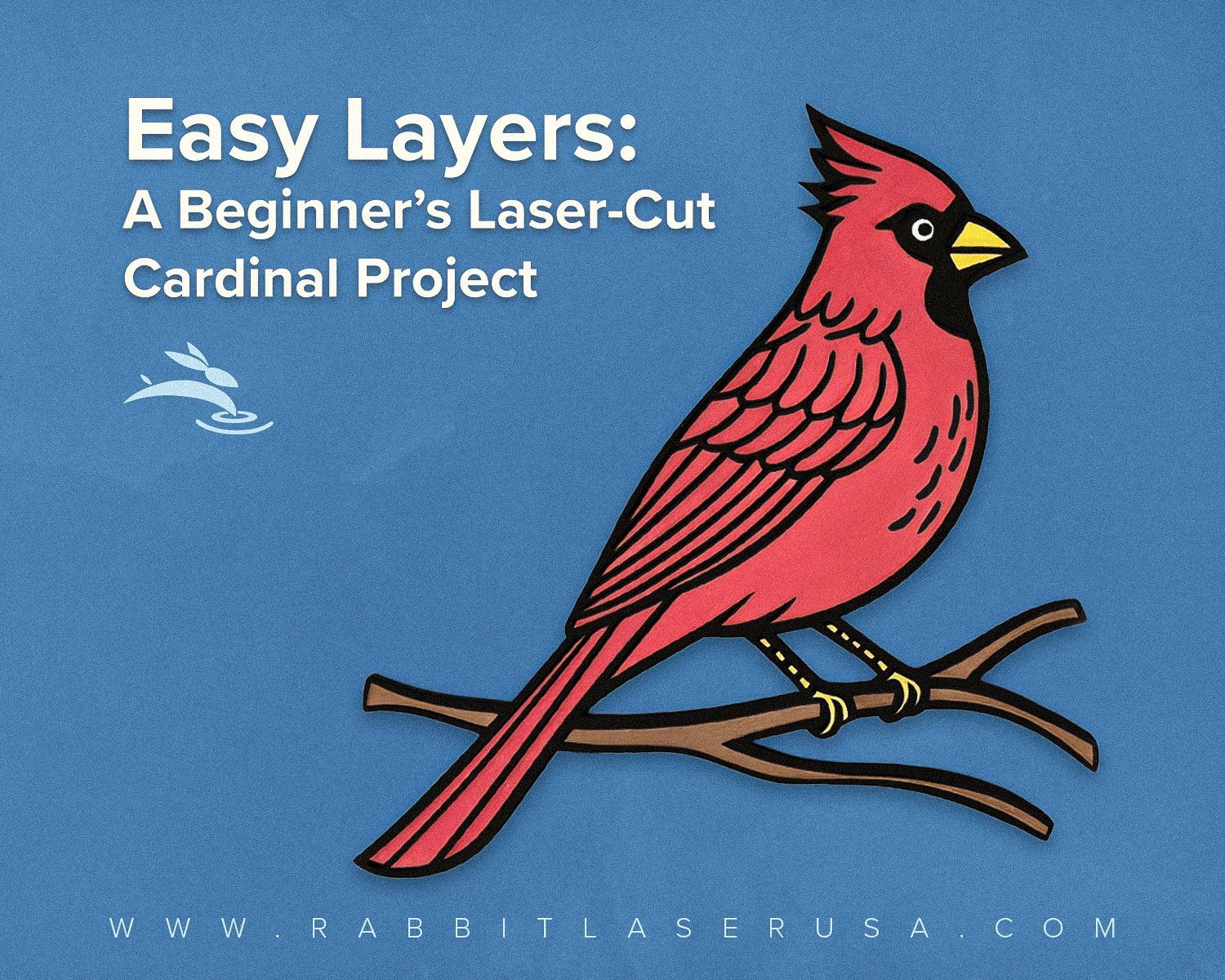
CNC Laser Cutting: Precision at Its Best!
Introduction
In today's fast-paced manufacturing world, precision and efficiency are paramount. One technology that has revolutionized the industry by delivering exceptional accuracy is CNC laser cutting. By combining computer numerical control (CNC) with high-powered lasers, this method has set new standards in precision cutting. This article delves into the intricacies of CNC laser cutting, exploring its advantages, applications, types, and much more.
What is CNC Laser Cutting?
CNC, or Computer Numerical Control, refers to the automation of machine tools through computers executing pre-programmed sequences of machine control commands. Laser cutting, on the other hand, utilizes a high-powered laser beam to cut materials. When combined, CNC laser cutting employs computer controls to direct the laser beam, allowing for precise and intricate cuts.
There are several types of lasers used in CNC cutting, including CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and Nd lasers. Each type has its unique properties and is suited to different applications.
Advantages of CNC Laser Cutting
The advantages of CNC laser cutting are numerous:
- High Precision and Accuracy: CNC laser cutting can achieve incredibly tight tolerances, making it ideal for intricate designs and complex shapes.
- Speed and Efficiency: The process is significantly faster than traditional cutting methods, reducing production times.
- Versatility in Materials: CNC laser cutters can handle a wide range of materials, from metals and plastics to wood and textiles.
- Minimal Waste and Eco-friendliness: With precise cutting, material waste is minimized, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing process.
Applications of CNC Laser Cutting
CNC laser cutting is used across various industries due to its precision and efficiency:
- Automotive Industry: For cutting body panels and intricate components.
- Aerospace Industry: Essential for producing lightweight, high-strength parts.
- Electronics and Electrical Industry: Used for creating precise circuit boards and enclosures.
- Medical Device Manufacturing: Ensures the production of accurate and reliable medical tools and devices.
- Art and Design: Enables artists and designers to create detailed and intricate pieces with ease.
Types of CNC Laser Cutters
There are different types of CNC laser cutters, each suited for specific tasks:
- CO2 Laser Cutters: Ideal for cutting, engraving, and boring non-metal materials.
- Fiber Laser Cutters: Perfect for metal cutting due to their higher energy efficiency and faster cutting speeds.
- Nd Laser Cutters: Used for high-precision cutting and engraving of both metals and non-metals. Nd lasers are known for their high peak power and short pulse durations, making them suitable for applications requiring fine, detailed work.
Materials Suitable for CNC Laser Cutting
CNC laser cutters can work with a variety of materials:
- Metals: Including steel, aluminum, brass, and more.
- Plastics: Such as acrylic and polycarbonate.
- Wood and Composites: Ideal for intricate designs and structures.
- Textiles and Leathers: Used in fashion and upholstery industries.
The CNC Laser Cutting Process
The CNC laser cutting process involves several steps:
- Design and Programming: Creating a digital design and programming the CNC machine.
- Setting Up the Machine: Preparing the machine with the appropriate settings and material.
- Cutting Process: The laser cutter follows the programmed path to cut the material.
- Post-Processing: Cleaning and finishing the cut pieces.
CNC Laser Cutting vs. Traditional Cutting Methods
When compared to traditional cutting methods, CNC laser cutting offers several benefits:
- Mechanical Cutting: CNC laser cutting provides higher precision and is faster.
- Waterjet Cutting: While waterjet is versatile, laser cutting is often more precise and cleaner.
Innovations in CNC Laser Cutting Technology
The field of CNC laser cutting is continuously evolving with new technologies:
- Advanced Laser Technologies: Improved lasers for better performance and efficiency.
- Automation: Integration with automated systems for increased productivity.
- Software Improvements: Enhanced software for more accurate and complex cutting.
Cost Considerations in CNC Laser Cutting
When considering CNC laser cutting, it’s important to understand the costs involved:
- Initial Investment: The cost of purchasing the machine.
- Operating Costs: Energy consumption and labor costs.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Regular upkeep to ensure optimal performance.
- Cost-Efficiency: The overall savings from reduced waste and faster production times.
Safety Measures in CNC Laser Cutting
Safety is crucial in CNC laser cutting:
- Protective Equipment: Use of safety goggles and protective clothing.
- Safe Operation Practices: Following safety protocols to prevent accidents.
Environmental Impact of CNC Laser Cutting
CNC laser cutting is more environmentally friendly than many traditional methods:
- Reduction in Material Waste: Precise cuts lead to less waste.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern lasers are designed to be energy-efficient.
- Eco-friendly Materials: Use of sustainable materials further reduces environmental impact.
Choosing the Right CNC Laser Cutter
Selecting the right CNC laser cutter involves several factors:
- Material and Thickness: The type and thickness of material you will be cutting.
- Precision Requirements: The level of detail needed in your cuts.
- Making the Best Choice: Evaluating your needs and budget to choose the right machine.
Future Trends in CNC Laser Cutting
The future of CNC laser cutting looks promising with various trends emerging:
- Industry Growth: Continued expansion of the CNC laser cutting market.
- Emerging Technologies: Innovations such as 3D laser cutting.
- New Applications: Potential uses in new industries and fields.
Conclusion
CNC laser cutting represents the pinnacle of precision in manufacturing. Its ability to deliver high-quality, accurate cuts across a variety of materials makes it indispensable in many industries. As technology continues to advance, CNC laser cutting will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in the future of manufacturing. 🐰
FAQs
What materials can be cut with CNC laser cutting?
CNC laser cutting can handle a variety of materials, including metals (steel, aluminum, brass), plastics (acrylic, polycarbonate), wood, composites, textiles, and leathers.
How does CNC laser cutting compare to traditional cutting methods?
CNC laser cutting offers higher precision, faster speeds, and cleaner cuts compared to traditional mechanical and waterjet cutting methods.
What are the safety measures for CNC laser cutting?
Safety measures include using protective equipment like goggles and following safe operation practices to prevent accidents.
What are the cost considerations for CNC laser cutting?
Costs include the initial investment for the machine, operating costs, maintenance, and potential savings from reduced waste and faster production times.
What are the future trends in CNC laser cutting?
Future trends include industry growth, emerging technologies like 3D laser cutting, and new applications in various fields.





Quick Links
Copyright © 2023 | All Rights Reserved | Rabbit Laser USA